We’ll review the importance of Magnesium (Mg) in cannabis cultivation, from its basic functions to signs of deficiency and excess, as well as best practices for ensuring an adequate supply of this essential nutrient.

Mg functions in Marijuana
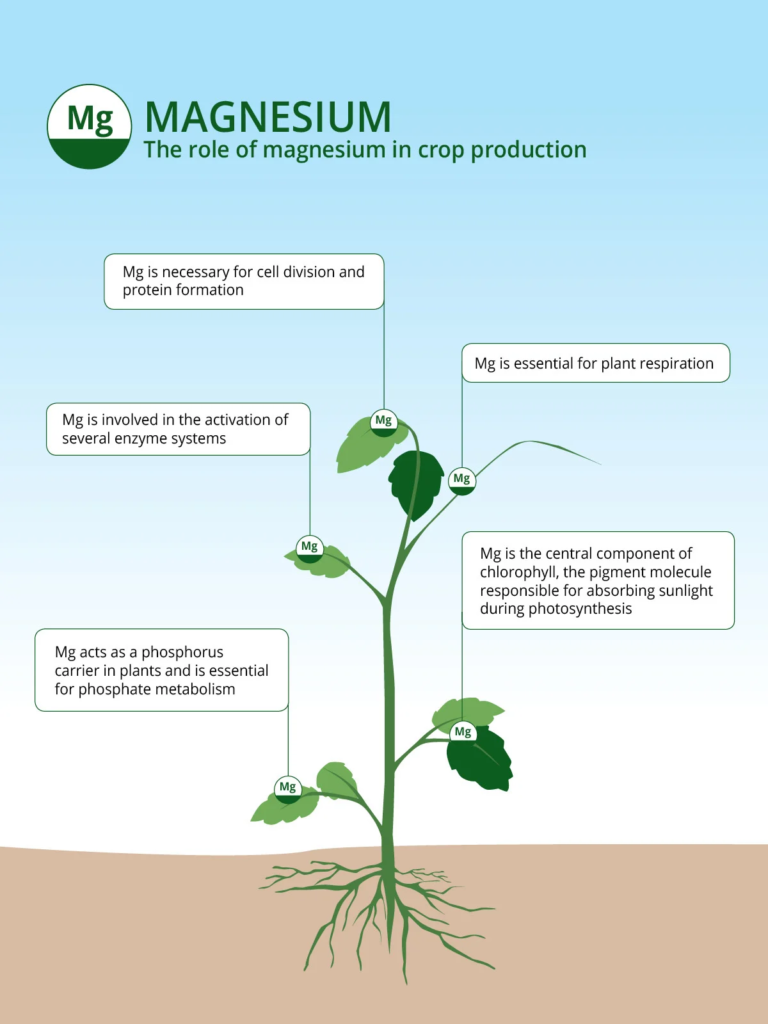
Mg is a secondary nutrient that is essential for all life stages of the plant and is required in large quantities. It is the central atom of chlorophyll and has a direct impact on the absorption of solar energy so that it can be subsequently processed and used by the plant to create carbohydrates (and sugars).
The plant absorbs Magnesium in form of ion, Mg2+ (Magnesium cation, a mineral nutrient essential for life). It is present in all cells of all organisms. Its cationic form of magnesium is the one found in the soil.
Therefore, how do we proceed when growing in soil or hydroponics to control Mg levels in the substrate? Since it’s a mineral, we can provide it through a Magnesium mononutrient or other products that contain a high proportion of Mg, allowing direct absorption by the roots without having to wait for the microbes to transform it into a plant-assimilable fertilizer.

Mg deficiency in cannabis cultivation
If the substrate pH is below 7.0, Magnesium can be easily absorbed by cannabis plants. However, if the substrate is very acid, with a pH below 5.0, its availability will be much lower or nonexistent; in this case, the substrate’s pH must be increased.
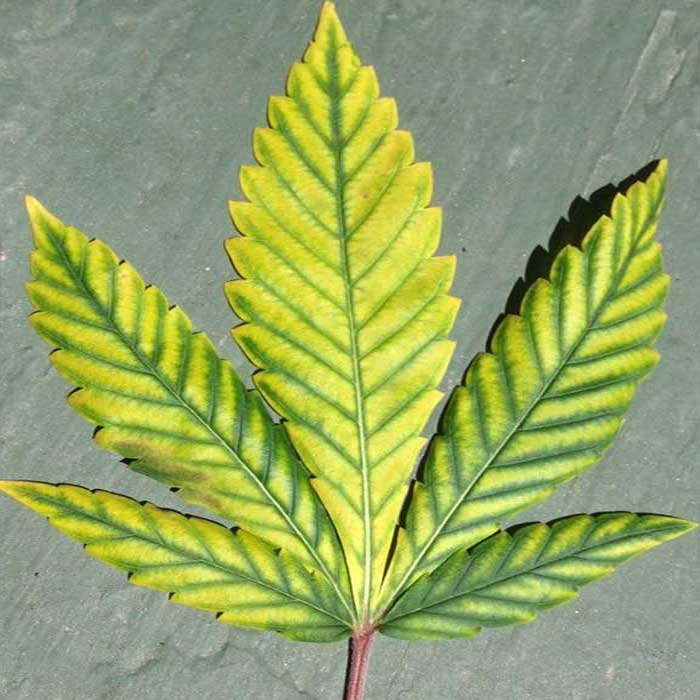
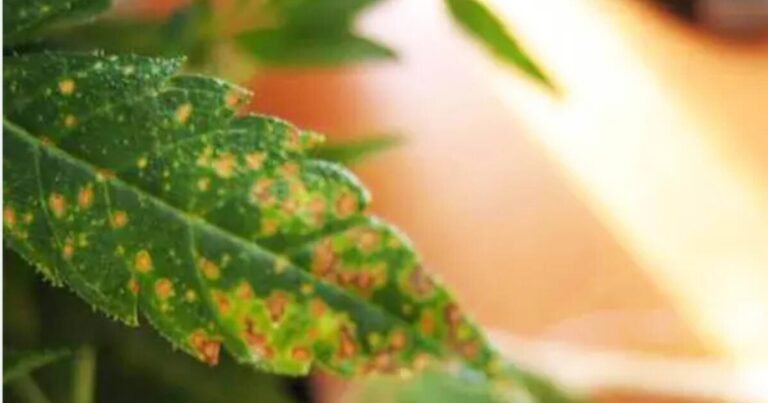
Mg is a mobile element, so deficiencies in this nutrient will first be visible in the older and lower leaves of the plant. As the deficiency progresses, the central part will also be affected by the lack of this element.
Magnesium is a nutrient that, just like Nitrogen (N), is easily removed by abundant water, with an EC of 0.0 to 0.4 (Electroconductivity).
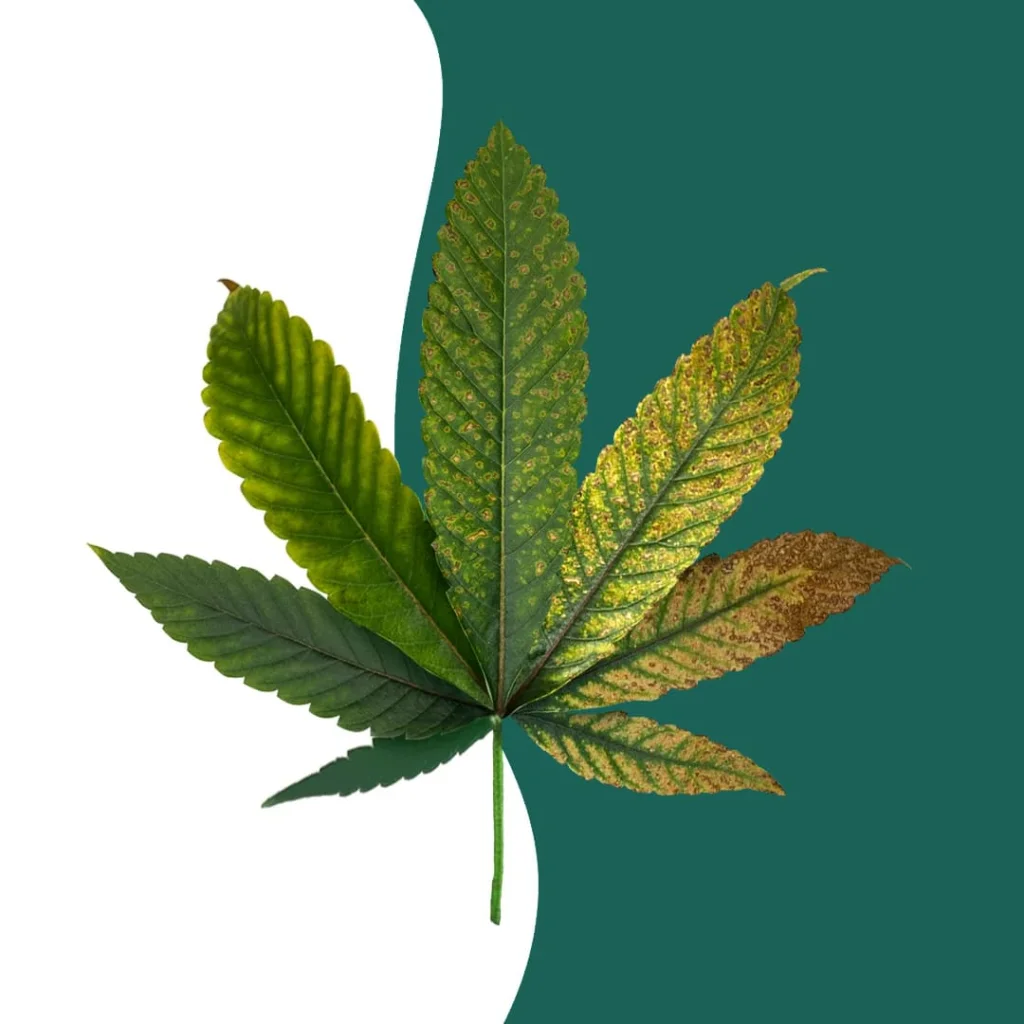

Stages of Mg deficiency in Cannabis
This blockage usually occurs during the firsts weeks of flowering, when the plant is beginning to form buds. Between the 3rd and 6th week of flowering, if there is an excess of fertilizer, the plants will try to absorb as much of the available nutrients as possible, causing an over-fertilization of K (Potassium), which will block Mg absorption. If this happens, flush the roots.
It’s important to note that the deficiency often occurs because the substrate doesn’t have enough Magnesium. If this is the case, fertilize with a little more than the usual dose.
To quickly detect Mg deficiency in cannabis plants, you should keep in mind that:
- During the early stages of deficiency detection is difficult.
- Deficiencies occur in the oldest and lowest leaves of the plant.
- The tips of the leaves turn brown, curling upward.
- Brown spots increase, progressing from the bottom to the top of the plant.
- The youngest leaves located at the top of the plant are affected by a large brown spot along with possible discoloration of the veins.
- Deficiency can be caused by an accumulation of other nutrients such as Ca and K.
- Mg Sulfate can be easily applied to help eradicate the deficiency quickly with a dose of 2% Mg concentration and 7.1 pH.
- Root and ambient temperatures shouldn’t be bellow 18ºC (64.4 F) at night and 24ºC (75.2 F) during the day.
- The substrate pH in soil should be adjusted to 6.5 and in hydroponics to 5.5 for about five days if the deficiency is significant.

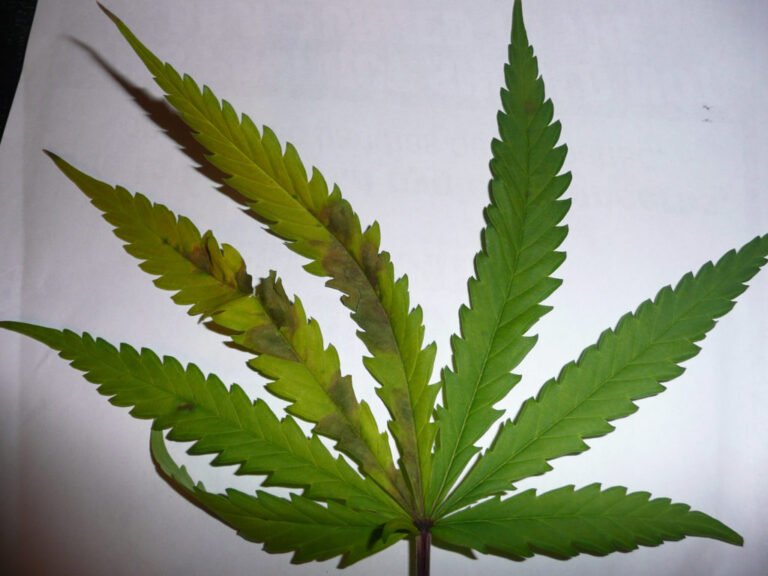
Mg Excess
Mg excess in cannabis plants can manifest itself through several symptoms, including poor growth, dark green leaves, or even brown spots on the edges.
To correct this problem, it is essential to balance the pH soil and adjust fertilization levels to reduce the concentration of the macronutrient.
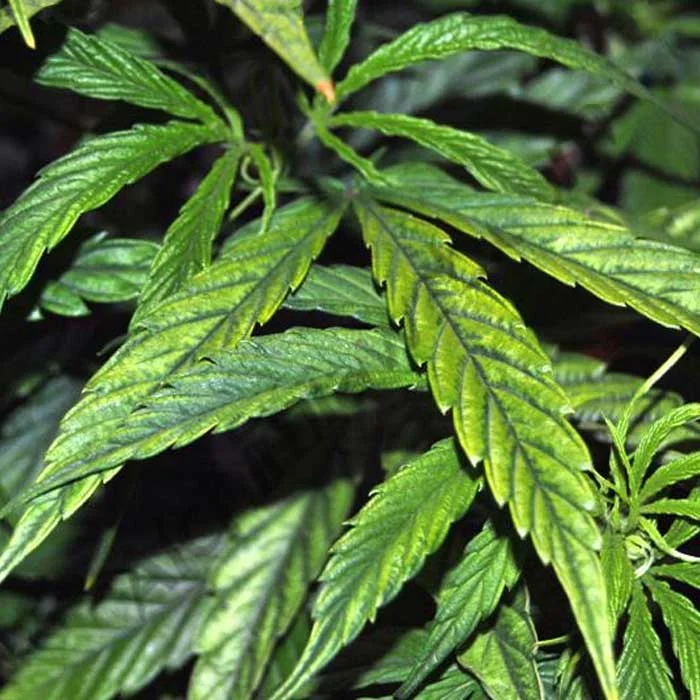

To quickly detect Mg excess in cannabis plants you have to keep in mind that:
- It’s difficult to detect because Mg excess is uncommon if we use appropiate substrates for marijuana cultivation.
- Magnesium ion (Mg2+) conflict with the Calcium ion (Ca2+), producing Ca blockage (you can read Calcium deficiency symptoms in our english blog).
- If there’s Mg excess, a root flush should be performed, applying at least three times the pot’s capacity and then watering with a balanced fertilizer.