We’ll explore the complexities and benefits of Nitrogen (N) in the Cannabis cultivation process.
Nitrogen (N) is a macronutrient and one of the most important elements in cannabis cultivation, as it promotes healthy and vigorous growth; and, of course, it cannot be missing from any crop.

Nitrogen (N) in cannabis cultivation
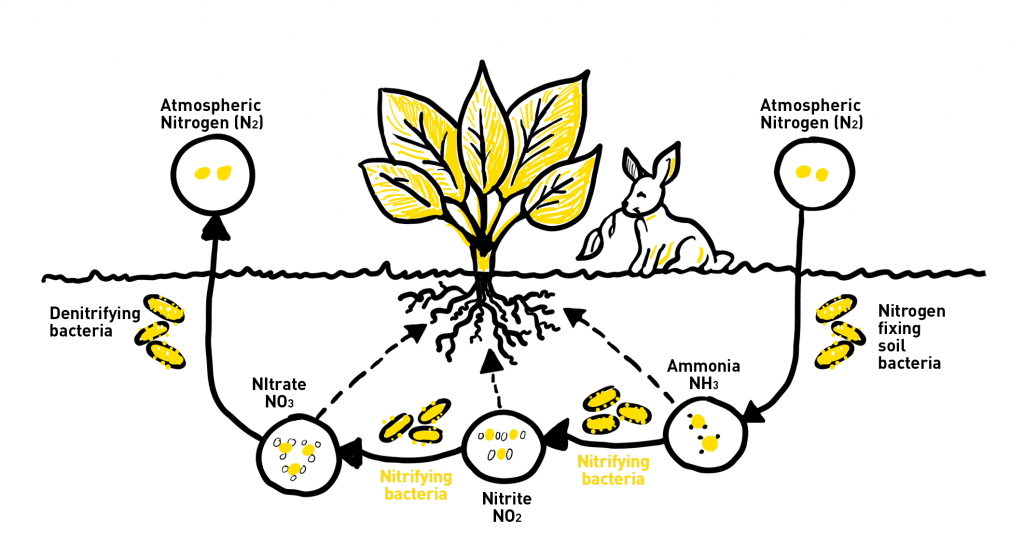
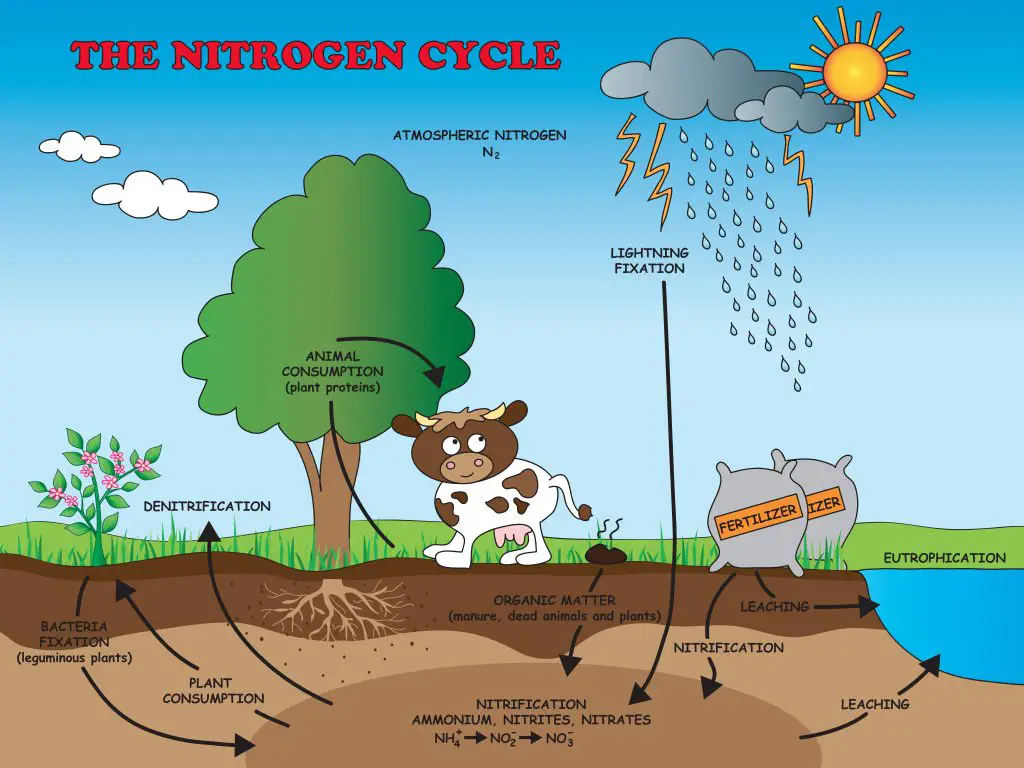
N is a very important mobile element that directly interacts in the development of cannabis plants through all their life stages. Depending on the plant’s life stage, it will have more or less demand for this nutrient.
N regulates cannabis plants’ ability to produce proteins, amino acids, enzymes, chlorophyll, alkaloids, and nucleic acids. Also is primarily responsible for stem, leaf and branch growth and overall vigor of the plant.
Nitrogen can be found in different forms: organic, ammonium and nitric. The difference between these forms is the speed at which plants absorb N. Ammonium is the fastest-absorbing form and consequently, the one that can most easily produce excesses of the macronutrient. The Nitric form is also easily absorbed by plants, but it’s not as easy as the Ammonium one. For this reason, in bottles of liquid fertilizers, we find N mixed in both forms to balance plant absorption without causing excess or deficiency of this nutrient.
It’s important to consider that if plants’ demand for N exceeds the N available to them, they will suffer a deficiency. On the other hand, if the levels of this element exceed what the plant needs, it will suffer overfertilization.
Fertilizers can be found in two forms: mineral and organic. The first one it’s absorbed faster by plants because it doesn’t need to be previously processed by the microbial life that lives in symbiosis with the ground to be absorbed by plants.
You can find N-rich fertilizers in both liquid and solid forms.
An optimal Nitrogen level in plants will results in:
- Vegetative vigor.
- Bright green color in leaves due to chlorophyll production.
- Increase number of plant leaves, stem length, fruits, and seeds.
- Greater plant resistance to fungi.
- Greater plant resistance to insects.
- Greater resistance to frost and hail.
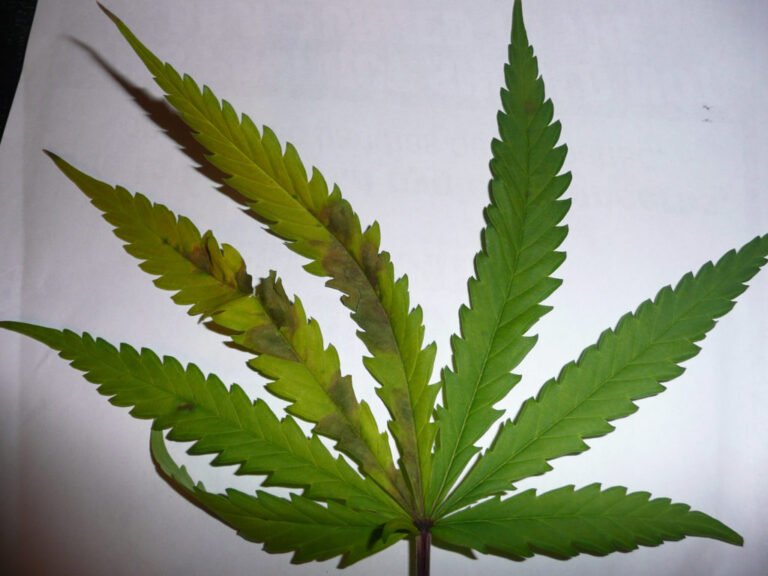
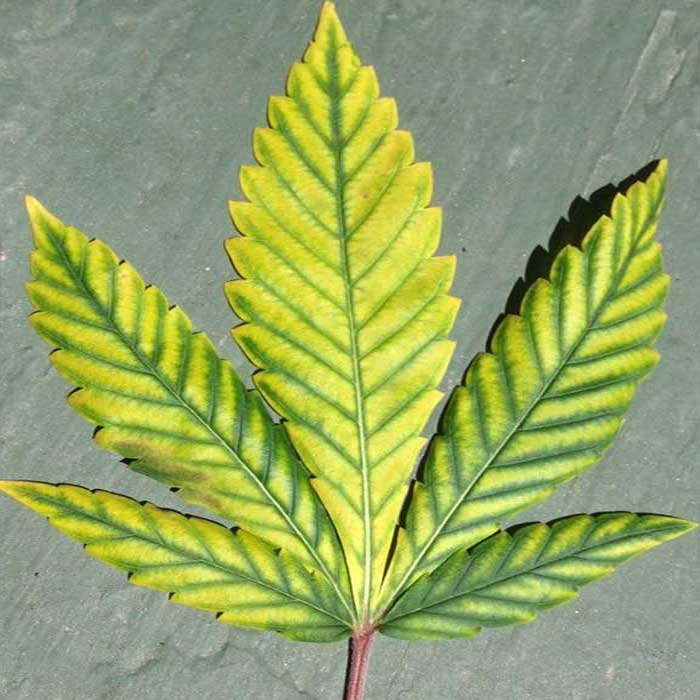
Nitrogen deficiency in cannabis
When cannabis plants don’t have balanced nutrition and there is a lack of this element, abnormalities in their development occur that are visible through the morphology of the plant, which we call deficiencies.
- Plant growth is slower.
- The leaves gradually turn yellow, starting at the bottom of the plant. Chlorosis begins at the tips and thins toward the center of the leaf.
- Plants have fewer defenses against pests, diseases, and stress.
- Flowering and seed production are severely affected.
- Massive defoliation occurs after advanced chlorosis.
- The deficiency progresses from bottom to top, ultimately affecting the youngest leaves.
To quickly resolve the problem, a liquid N-rich fertilizer should be added to the irrigation water so that the plants can recover their optimal levels of this nutrient a few days after.
It’s important to know that once there is a deficiency of N in cannabis, the production of the plant will be already damaged. Because of it, it’s important to mantain a balanced diet throughout the crop to achieve optimal quality and yields.

N Excess in Marijuana Plants
On the other hand, Nitrogen excess in cannabis also has repercussions, reducing flower production and quality. These excesses can be recognized by observing the following symptoms:
- Excessive foliage on the plant.
- Weak stems.
- Delayed ripening of the flower, making it less sweet.
- Claw-shaped leaves facing the ground.
- Poor flower combustion.
- Very deep green leaves.
- Low resistance to pests in general.
To solve this problem you should perfom a root flush using three times the pot’s capacity along with a low electroconductivity (EC). You need to measure the output EC to determine how saturated the substrate is with salts. In extreme cases, continue flushing until the substrate’s nutrient levels are the same as the water used for the wash.

How does cannabis recover from N excess?
Cannabis plants, as we have already mentioned, are capable of show us morphologically talking it’s vital state. It will be easy to know the state of our plant though their leaves, color, shape, etc.
In case of a overfertilization or a deficiency of the same element, the cannabis plant will always take a few days to recover. The time to recover completely will depend on the degree of deficiency or excess that the plant may has. Early detection will always help to recover in a shorter time.
Depending on the substrates and fertilizers used, plants may recover faster or slower. In hydroponic growing systems, the plant’s recovery rate will be faster than in soil grown with organic fertilizers.
During the growth phase and in case of a slight overfertilization, when there is an excess of N, we will reduce or eliminate the growth fertilizer durin g a few waterings.
During the bloom phase, if we overfertilize, we should proceed according to the growing week we are. If this happen during the first two weeks after the photoperiod change, we will proceed just as if we were in growth phase. This is because plants will continue to grow almost until the third week, when the flowers begin to appear.
However, if we are already in bloom phase, excess N is not usually as common. But, if there is an excess, we should eliminate the base fertilizer and continue fertilizing only with a PK (Potassium and Phosphate) supplement, which does not contain N added. After that, the plants will be able to create flowers according to their phase and at the same time eliminate excess of the element. In the case of more pronounced overfertilization, we can first perform a root wash to clean the substrate a little of the excess nutrients and then water with the appropriate doses of PK until indicated on the product label.