Plant nutrition is a key aspect for proper plant development and Calcium (Ca) plays an important role in the development and health of cannabis crops.

Calcium and Cannabis
Ca is a chemical element found in the human body and in plants. It is a secondary nutrient of great importance given the large quantities required by the plant throughout its growth.
From the very beginning, durinf the seed germination stage, Ca plays a direct role in root development and participates directly in protein synthesis, while also being an active ingredient for enzymes. It is absorbed by the roots in the form of the Ca2+ ion (the chemical formula of ionic calcium, a divalent cation with two positive charges).
This macronutrient supports other elements that, when combined, participate in different metabolic processes, such as the creation of vitamins in this case vitamin B12. These vitamins adhere to and form part of the cell walls of plant tissues, making them more resistant to pathogen attacks and maintaining the vitality and activity of their cells.

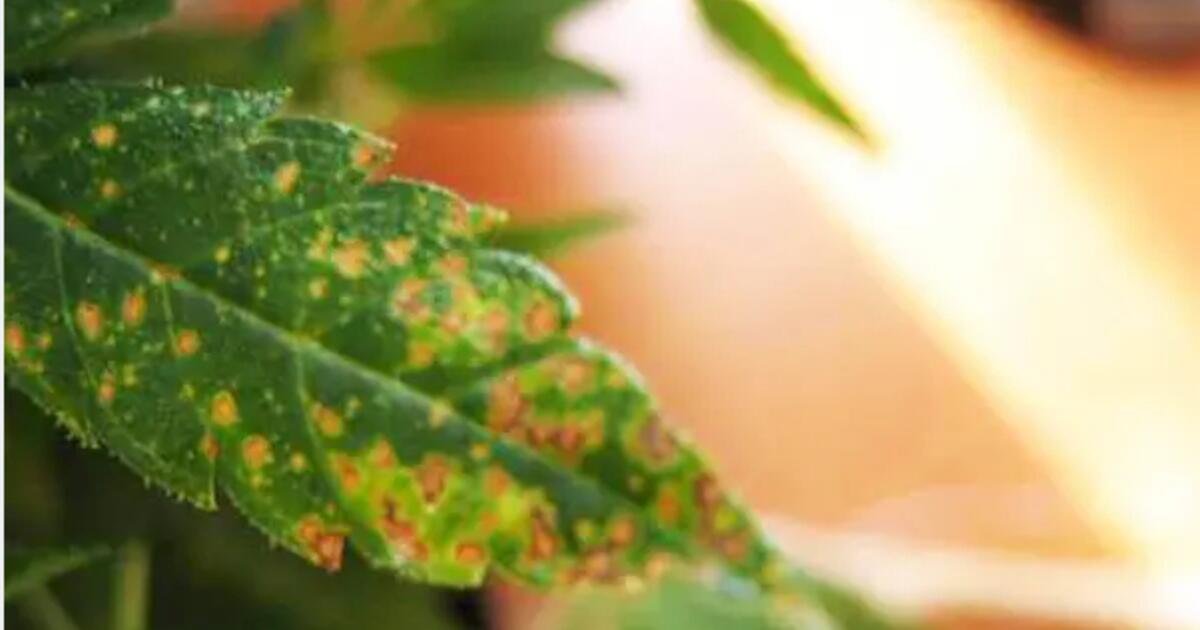
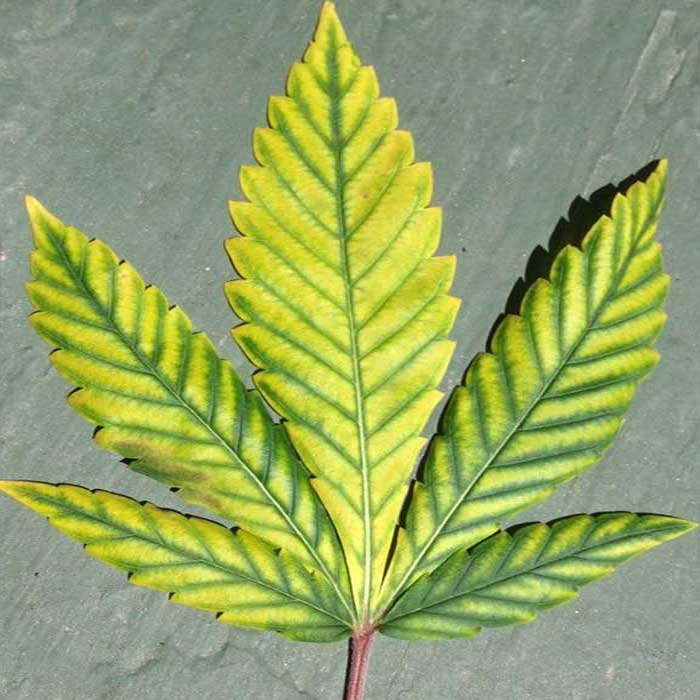
Beggining of Calcium deficiency
Functions of Ca in Cannabis Plants
- Calcium is necessary for the development of cell walls in the root system.}
- It is an immobile element that aids in the breakdown of organic matter for the plant’s assimilation of nutrients.
- It acts as a bridge between humus and nutrients.
Calcium Deficiency
Calcium is an element that is easily found in the soil. It is abundantly available to plants, and deficiencies of this element are not common except in soils with a very acid pH.
Deficiencies may be more prevalent in hydroponic crops since the substrate used is inert (coconut, clay, rock wool).
In these cases, we must ensure that the plant’s Ca intake is adequate to avoid deficiencies from the outset.
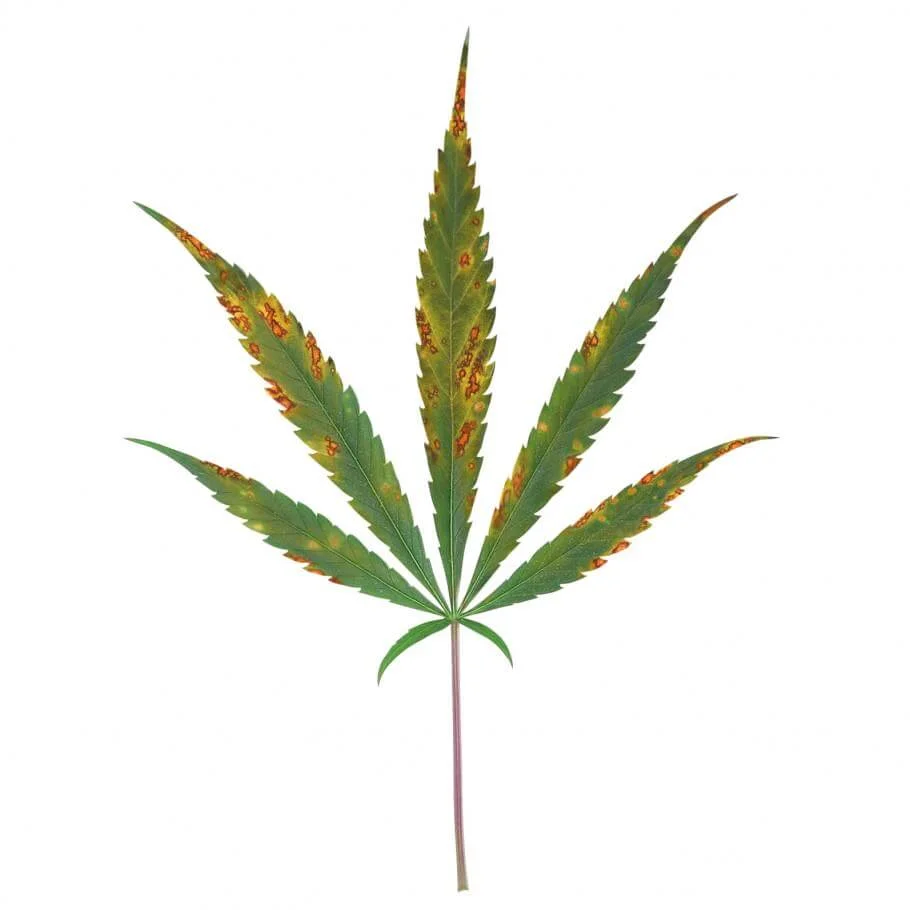

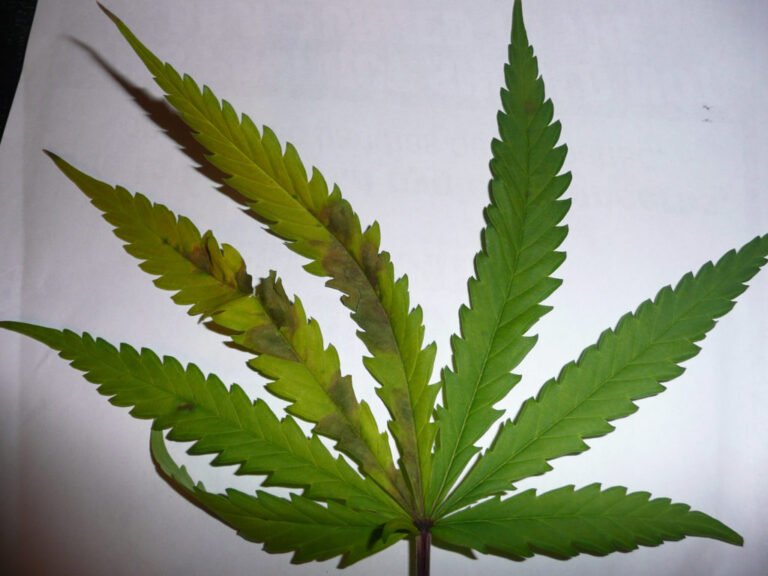
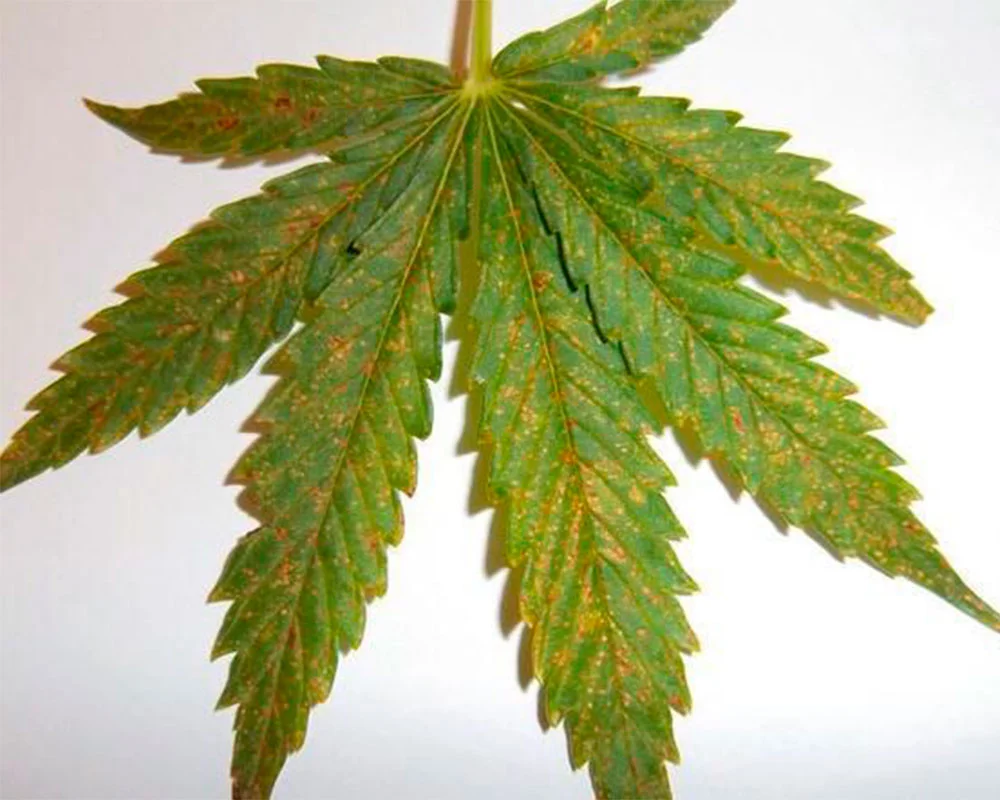
Medium Stage of Ca deficiency
Before applying any fertilizer, it should be considered that two parts of Ca are required for one part of Mg (Magnesium), so the EC ranges from 0.0 to 0.3-0.4 (Electroconductivity).
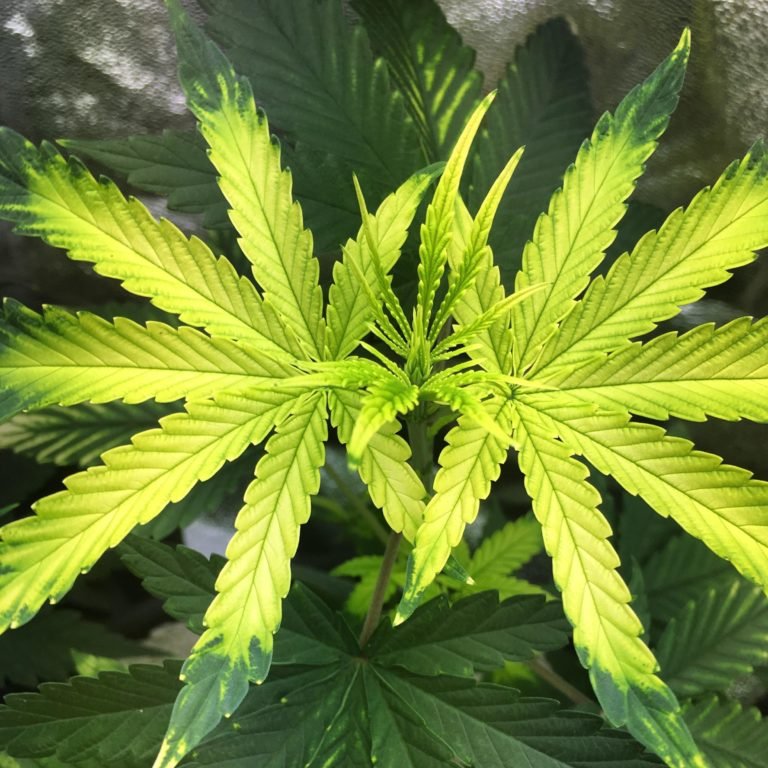
Visible symptoms of Ca deficiency in cannabis:
- The youngest leaves of the plant are the first to be visibly affected.
- The development of the upper part of the plant is delayed.
- The root system is affected, reducing the fertilizer absorption.
- As long as the deficiency progresses, the youngest leaves appear yellowish and will become deformed.
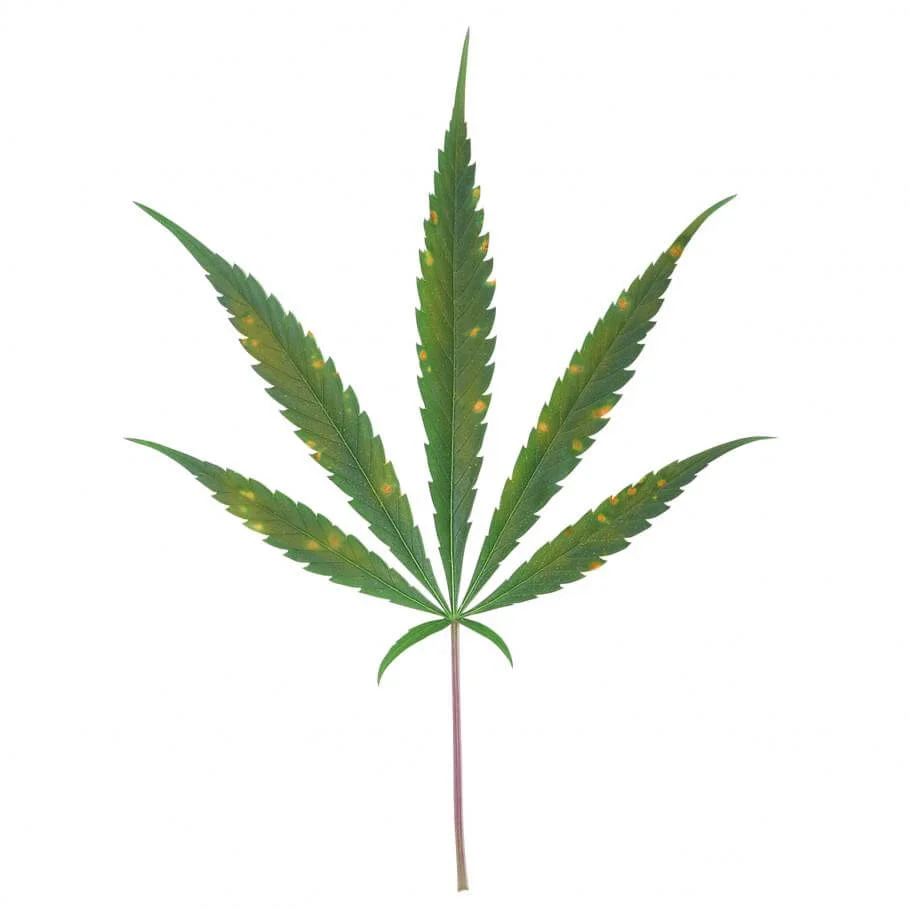
- Bud production is severely reduced.
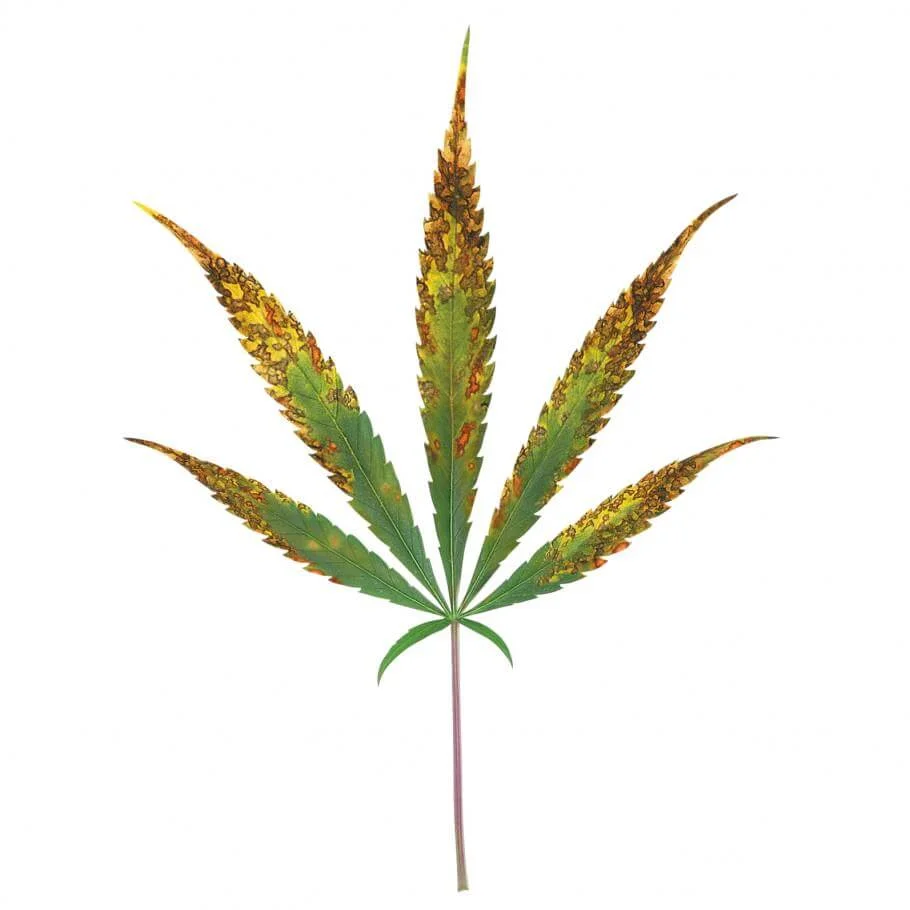

Advanced stage of Calcium deficiency.
Ca Excess
Calcium excess is difficult to detect; it causes the blockage of several nutrients, creating deficiencies in Potassium (K), Magnesium (Mg), Manganese (Mn), and Iron (Fe).
In various hydroponic growing systems, when there is Ca-excess in the tank, it comes into contact with the Sulfur in the irrigation water, precipitating and settling at the bottom of the tank. In this case, the water in the tank must be changed to adapt it to the needs of the crop.
Ca is an element directly related to plant transpiration. This transpiration control comes from the roots and stomata, located in the leaves and through which the plant transpires. Often, the stomata may close due to excess heat, causing a superficial burn, which is mistaken for a symptom of deficiency.
It is worth noting that with a deficiency of this element, plants are always more susceptible to heat stress because Calcium contributes to the creation of proteins that make the plant more resistant to heat.
How to provide Calcium to marijuana plants?
If purified water is used, since it contains no nutrients, its initial EC will always be 0.0.
Marijuana fertilizers already contain the trace elements necessary for the plant’s life, but some nutrients such as Ca or Mg must have a higher initial concentration to ensure the plants receive the correct amount of these nutrients.
If we use tap water with an EC of 0.3-0.4, it will be an adequate EC to mix it with fertilizers.