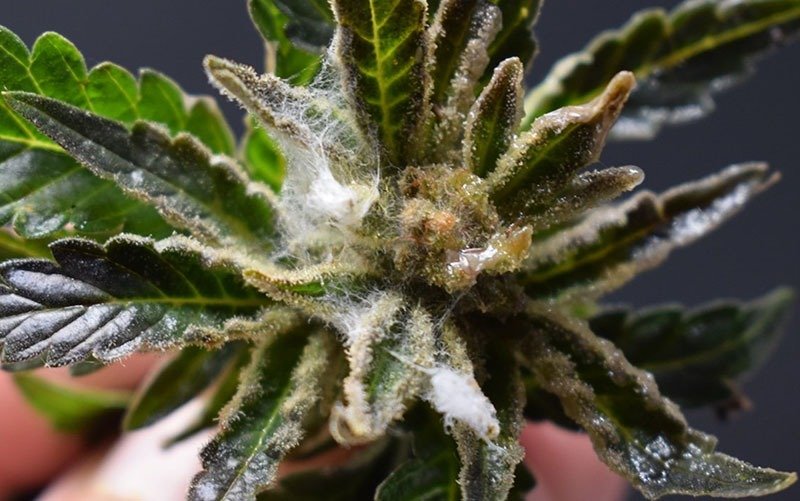
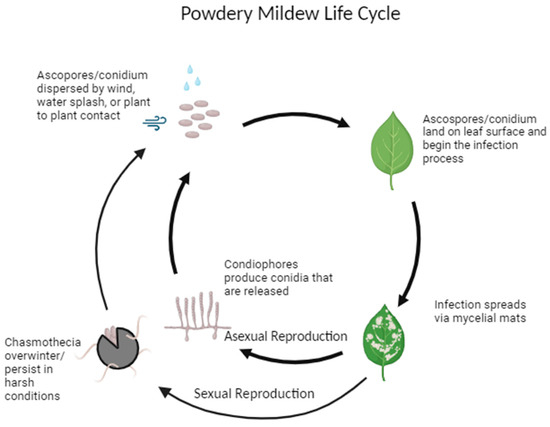
Today, cannabis plants are increasingly susceptible to Powdery Mildew. This infection is easy to cure but it could have serious consequences as it can completely damage crops.
The first phase develops on the leaves, then it moves to the petioles, trunks and finally the buds, completely destroying the resin as buds with fungal spores cannot be smoked.
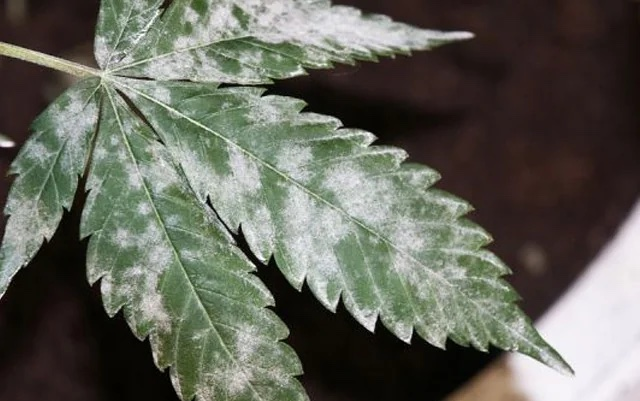

The pest affects indoor cannabis cultivation as well as outdoor or greenhouse crops. Its spread requires strong humidity fluctuations, going from low to high relative humidity. This situation is very common in crops under artificial lighting and in greenhouses. Outdoors, the pest is more seasonal and in spring or autumn.
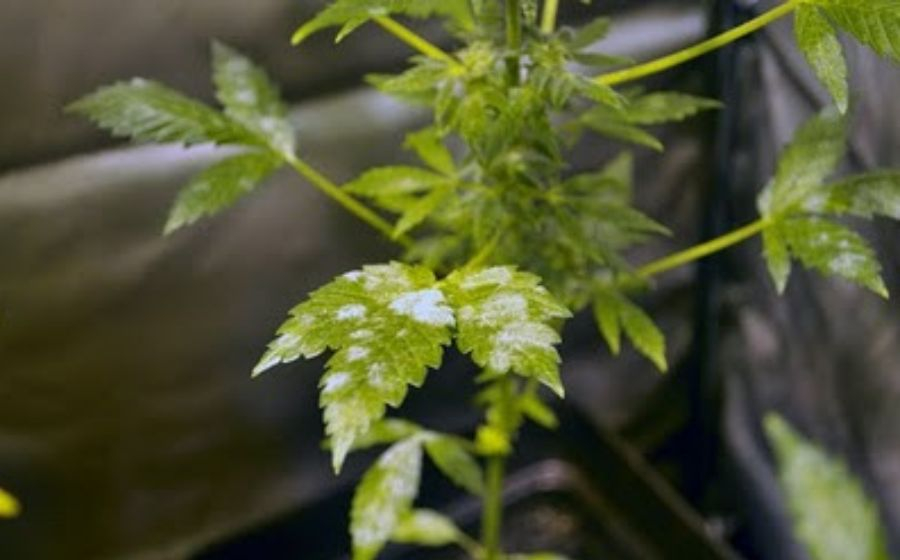
It manifests as a very typical white powder or ash, which can be confused with dust on leaves and shoots. In its second phase, the affected leaves turn yellowish and eventually dry out.
Powdery Mildew is an external fungus, and its behavior is very similar to that of sucking insects, as its small spores are carried by the wind. When they land on a leaf, they sprout roots that suck and absorb nutrients from the plant.
Powdery Mildew in indoor crops
In indoor crops Powdery Mildew is a very common disease, and in some cases it’s necessary to take preventative measures from the start of the grow. However, what will help us most avoid fungal contamination is controlling the climate in our growing space. Don’t exceed 65% relative humidity or let it drop below 40%. With a humidifier, you can prevent the humidity from dropping too low when the lights are on due to the heat from the light.
During the plants’ nighttime rest, adjust the ventilation so that the plants’ respiration doesn’t produce condensation inside the space. In extreme cases, you can resort to using a dehumidifier. Another detail that can help us prevent the spread of the fungus is to plant cannabis plants not too close of each other, then you can avoid shady areas forming in the lower parts of the plants, which favor the appearance of Powdery Mildew.
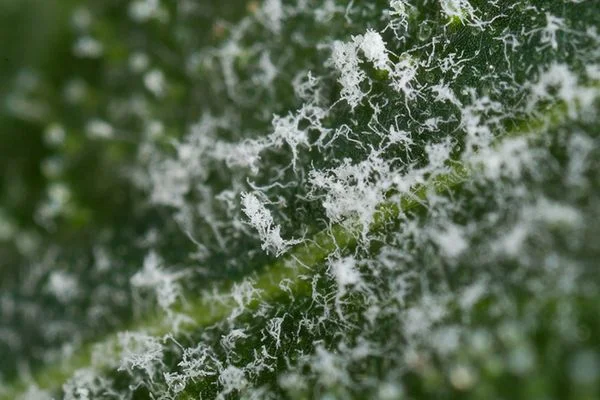

Powdery Mildew in Outdoor and Greenhouse crops.
In outdoor cannabis cultivation this infection is a relatively seasonal disease, with spring and especially fall being the seasons most probably to get infected. To prevent it, keep plants free of dry leaves and avoid planting them in areas with limited sunlight. If growing in pots, it’s a good idea to rotate the pots so that all parts of the plants have good sunlight exposure. Plants shouldn’t be planted too close together. Air circulation between plants is important.
In greenhouses, proper air circulation is essential. To achieve this, it’s highly recommended to install fans inside the greenhouse to force air circulation.
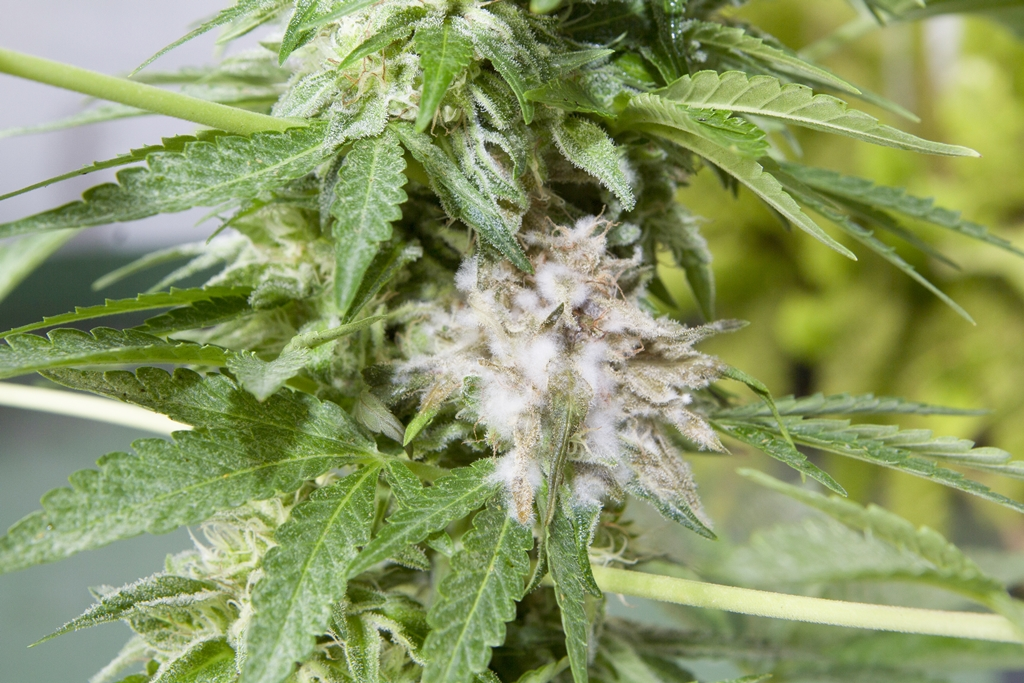


Powdery Mildew Control
Among the biological treatments for Powdery Mildew control is Anasac Powdery Mildew Fungicide, a curative and preventative wettable powder product, which is effective controlling the fungus that attack roses, peach trees, grapevines, currants, dahlias, begonias, oaks, cannabis, shrubs, and garden trees.
Dose and Directions for Use
Dissolve 10 g in 1 L of water and then spray it on leaves, stems, and branches. Powdery mildew can be prevented by applying this product preventively. To achieve this, apply every 20-30 days in spring-summer and early fall, especially after rains. If powdery mildew is already present, a second application is recommended 10 days later.
The treatment should be continued until 10-15 days before harvest.
Prevention is better than cure, so I recommend using these products during growth and until the end of pre-flowering and avoid spraying the buds with any substance!










